Posted by Chrom Tech on 28th Oct 2025
What Is Endcapping in HPLC Columns
By Chrom Tech – Your Chromatography Consumables Partner Since 1983
Understanding Endcapping in HPLC Columns
Endcapping is a key chemical modification that enhances the performance and stability of HPLC columns. It involves reacting the free silanol groups remaining on the silica surface after bonding with small trimethylsilyl (TMS) groups. This process reduces unwanted secondary interactions between analytes and residual silanol sites, improving peak symmetry, reproducibility, and column lifetime.
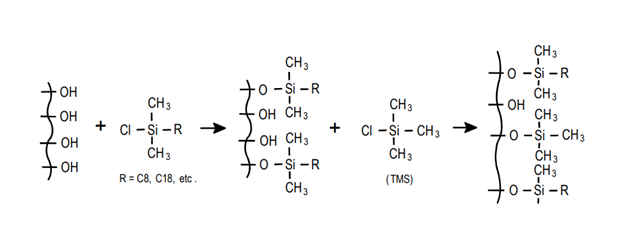
What Is Double Endcapping?
Double endcapping refers to repeating the endcapping process to further deactivate residual silanol groups. This extra treatment minimizes ion-exchange interactions and enhances column stability—especially in the mid-pH range (around pH 4–8), where single endcapping may not completely shield all silanols.
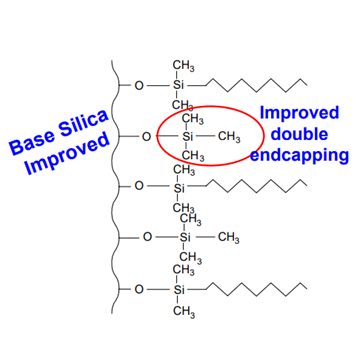
For analytical methods operating in neutral or slightly basic conditions, double or triple endcapped columns are preferred. They maintain consistent selectivity, reduce tailing for basic compounds, and protect the silica backbone from dissolution at elevated pH levels.
When to Use a Non-Endcapped HPLC Phase
Non-endcapped phases are ideal for low pH separations or when additional silanol activity is beneficial for selectivity. For instance, the Agilent ZORBAX StableBond line is a non-endcapped, sterically protected bonded phase designed for extreme acidic stability down to pH 1. This makes it an excellent choice for aggressive mobile phases and acidic analytes.
Agilent StableBond Sterically Protected Surface Reaction
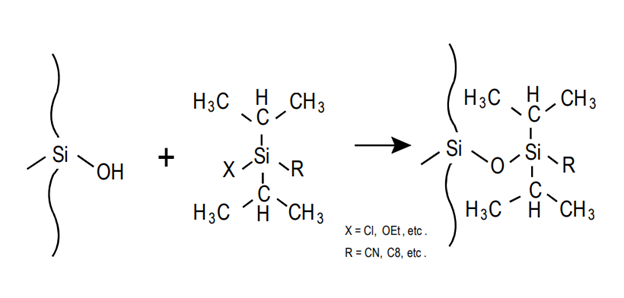
The StableBond series uses a unique sterically protected silane chemistry that resists hydrolysis, resulting in longer lifetimes under low pH conditions. Available selectivities include C18, C8, CN, Phenyl, and C3.
HPLC Columns for LC/MS Applications
When selecting HPLC columns for LC/MS systems, chromatographers prioritize sensitivity, resolution, and compatibility with the detector. Endcapped C18 phases are typically recommended for LC/MS because they reduce tailing of basic compounds and ensure cleaner ionization profiles.
Most LC/MS methods operate at low flow rates (µL/min to 1 mL/min) and use narrow-bore columns (e.g., 2.1 mm ID) to conserve solvent and increase sensitivity. For fast, high-throughput separations, the Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell 120 EC-C18 column offers outstanding resolution and backpressure control. Its larger frit design handles dirtier matrices such as plasma or serum without clogging.
Best Practices for Column Longevity
To extend the lifetime of your column, always match your mobile phase pH to the bonded phase’s stability range. Use endcapped columns for mid-pH applications, and non-endcapped columns for highly acidic methods. Incorporate preventive tools like HPLC syringe filters, HPLC guard columns, and Idex fittings to protect the column from particulates and contamination.
Need help choosing the right bonded phase or column type? Our technical specialists are here to help. Contact Chrom Tech Support for tailored recommendations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is endcapping in HPLC columns?
Endcapping replaces free silanol groups on the stationary phase with trimethylsilyl (TMS) groups to reduce silanol activity, improving peak shape and column lifetime.
What is double endcapping?
Double or triple endcapping repeats the silanol-capping process multiple times, further minimizing secondary interactions and enhancing column stability at mid pH ranges.
When should I use a non-endcapped column?
Use non-endcapped columns for acidic methods or when slight silanol activity enhances selectivity. Agilent ZORBAX StableBond phases perform reliably at pH values down to 1.
Which HPLC columns are best for LC/MS?
Endcapped C18 columns, like the Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell 120 EC-C18, provide excellent resolution, throughput, and durability for LC/MS workflows.
How can I extend my HPLC column’s lifetime?
Keep the mobile phase within the pH range recommended for the bonded phase, use guard columns and syringe filters, and avoid unnecessary exposure to extreme pH or pressure.

